Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sakon, Atsushi*; Nakajima, Kunihiro*; Takahashi, Kazuki*; Hohara, Shinya*; Sano, Tadafumi*; Fukaya, Yuji; Hashimoto, Kengo*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 247, p.09009_1 - 09009_8, 2021/02
In graphite-reflected thermal reactors, even a detector placed far from fuel region may detect a certain degree of the correlation amplitude. This is because mean free path of neutrons in graphite is longer than that in water or polyethylene. The objective of this study is experimentally to confirm a high flexibility of neutron detector placement in graphite reflector for reactor noise analysis. The present reactor noise analysis was carried out in a graphite-moderated and -reflected thermal core in Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). BF proportional neutron counters (1" dia.) were placed in graphite reflector region, where the counters were separated by about 35cm and 30cm -thick graphite from the core, respectively. At a critical state and subcritical states, time-sequence signal data from these counters were acquired and analyzed by a fast Fourier transform (FFT) analyzer, to obtain power spectral density in frequency domain. The auto-power spectral density obtained from the counters far from the core contained a significant degree of correlated component. A least-squares fit of a familiar formula to the auto-power spectral density data was made to determine the prompt-neutron decay constant. The decay constant was 63.3
proportional neutron counters (1" dia.) were placed in graphite reflector region, where the counters were separated by about 35cm and 30cm -thick graphite from the core, respectively. At a critical state and subcritical states, time-sequence signal data from these counters were acquired and analyzed by a fast Fourier transform (FFT) analyzer, to obtain power spectral density in frequency domain. The auto-power spectral density obtained from the counters far from the core contained a significant degree of correlated component. A least-squares fit of a familiar formula to the auto-power spectral density data was made to determine the prompt-neutron decay constant. The decay constant was 63.3 14.5 [1/s] in critical state. The decay constant determined from the cross-power spectral density and coherence function data between the two counters also had a consistent value. It is confirmed that reactor noise analysis is possible using a detector placed at about 35cm far from the core, as we expected.
14.5 [1/s] in critical state. The decay constant determined from the cross-power spectral density and coherence function data between the two counters also had a consistent value. It is confirmed that reactor noise analysis is possible using a detector placed at about 35cm far from the core, as we expected.
 on effective multiplication factor in 1/f
on effective multiplication factor in 1/f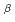 spectrum random system
spectrum random systemAraki, Shohei; Yamane, Yuichi; Ueki, Taro; Tonoike, Kotaro
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors; Transition To A Scalable Nuclear Future (PHYSOR 2020) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2020/03
We investigated the  dependence of the effective multiplication factor (k
dependence of the effective multiplication factor (k ) in the 1/f
) in the 1/f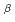 noise model. We conducted the two-group Monte Carlo calculations. We found that the standard deviation of the k
noise model. We conducted the two-group Monte Carlo calculations. We found that the standard deviation of the k distribution showed the positive correlation with the
distribution showed the positive correlation with the  value because the spatial distribution of the fuel became less uniform as the
value because the spatial distribution of the fuel became less uniform as the  value increased.
value increased.
Tada, Kenichi
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors; Transition To A Scalable Nuclear Future (PHYSOR 2020) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2020/03
The probability table is widely used for continuous energy Monte Carlo calculation codes to treat the self-shielding effect in the unresolved resonance region. The ladder method is used to calculate the probability table. This method generates a lot of pseudo resonance structures using random numbers based on the averaged resonance parameters. The probability table affects the ladder number. i.e., number of pseudo resonance structures. The ladder number has large impact on the generation time of the cross section library. In this study, the appropriate ladder number is investigated. The probability table of all nuclides prepared in JENDL-4.0 is used to investigate the appropriate ladder number. The comparison results indicate that the differences of the probability table are enough small when the ladder number is 100.
Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Nakajima, Kunihiro*; Takahashi, Kazuki*; Sakon, Atsushi*; Sano, Tadafumi*; Hashimoto, Kengo*
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors; Transition To A Scalable Nuclear Future (PHYSOR 2020) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2020/03
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) started the Research and Development (R&D) to improve nuclear prediction techniques for High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGRs). The objectives are to introduce a generalized bias factor method to avoid full mock-up experiment for the first commercial HTGR and to introduce reactor noise analysis to High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) experiment to observe subcriticality. To achieve the objectives, the reactor core of graphite-moderation system named B7/4"G2/8"p8EUNU+3/8"p38EU(1) was newly composed in the B-rack of Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). The core is composed of the fuel assembly, driver fuel assembly, graphite reflector, and polyethylene reflector. The fuel assembly is composed of enriched uranium plate, natural uranium plate and graphite plates to realize the average fuel enrichment of HTTR and it's spectrum. However, driver fuel assembly is necessary to achieve the criticality with the small-sized core. The core plays a role of the reference core of the bias factor method, and the reactor noise was measured to develop the noise analysis scheme. In this study, the overview of the criticality experiments is reported. The reactor configuration with graphite moderation system is rare case in the KUCA experiments, and this experiment is expected to contribute not only for an HTGR development but also for other types of a reactor in the graphite moderation system such as a molten salt reactor development.